Structural steel grades are essential construction materials designed for use in building and infrastructure projects. These steels are specifically engineered to provide strength, durability, and flexibility. They are composed primarily of iron and carbon, with small amounts of other elements to enhance their properties. Structural steel is available in various grades and is typically manufactured into specific cross-sectional shapes for different applications.
Table of contents
- What is Structural Steel?
- Producing & Testing of Structural Steel
- Properties of Grade E250
- Mechanical Properties of SS Grade E250
- Structural material grades Types
- What are The Different Grades of Structural Steel ?
- Structural Steel Standards
- Different Shapes of Structural cold formed steel
- Strength-Weight Ratio of Structural Steel
- Structural Steel vs Stainless Steel
- Yield Strength of Structural cold formed steel
- Tensile Strength of Structural beam
- Chemical Composition of Structural Steels
- E250 material Chemical Composition
- Advantages and Disadvantages of structural galvanized steel
- Benefits of Structural Steel Hollow Sections
- Characteristic of AISI 304 & 316
- S235 Steel Hollow Section Square Weight Chart
- S355 Steel Density kg/m3
- Mechanical Properties of Steel Grade E350
- E350 steel Chemical Composition
- Inspection Checklist of S235 Grade
- Structural Steel and Reinforcement Steel Difference
- Applications of S420 Material
What is Structural Steel?
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Construction material in various shapes |
| Profiles | I-beams, channels, angles, hollow sections |
| Fabrication Methods | – Hot Rolling: Shaping with heat – Cold Rolling: Shaping at room temperature – Welding: Joining sections – Bending: Creating curves |
| Applications | Buildings, bridges, roads, infrastructure projects |
Producing & Testing of Structural Steel
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | Alloy of iron and carbon |
| Production Methods | – Recycled Steel: Melting and refining – Raw Materials: Extraction from iron ore |
| Iron Extraction | – Process: Grinding taconite, magnetic separation – Iron Ore Characteristics: Raw ore is soft; carbon adds strength |
| Iron-Carbon Alloy Production | – Reduction Process: Heating coke with iron ore to bond carbon with oxygen – Carbon Content: Below 2.1% to form steel; structural steel has 0.05-0.25% carbon |
| Properties of Structural Steel | High strength-to-weight ratio 100% recyclable Cost-effective |
| Grades | Various grades with slight composition differences for specific needs |
Check Structural Steel Grade E250 Properties
Due to its remarkable properties as given below, it has become a premium construction material for infrastructure and skyline manufacturing. Find below the key points that highlight what properties it provides to products made using structural steel grade E250.
Properties of Grade E250
- Good weldability
- Good formability
- Good dimensional accuracy
- Toughness
- Heat treatable
- Sturdy construction
Mechanical Properties of SS Grade E250
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Yield Strength | 250 N/mm² |
| Tensile Strength | 410 N/mm² |
| Elongation | 23% minimum |
View the Standard Structural Steel Materials and Standards
It is a versatile and durable material that makes it highly useful in the construction industry. It is utilized due to its unique combination of properties. When choosing structural steel materials for specific applications, engineers consider the particular material to ensure outstanding performance and protection.
The following information about structural steel materials will give you a detailed understanding of this critical construction material.
Structural material grades Types
| Steel Type | Key Features | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steels | No major alloys; Cu ≤ 0.6%, Mn ≤ 1.6%, Si ≤ 0.6% | Structural pipes and tubing |
| High-Strength, Low-Alloy Steels | Mn up to 2%; trace Cr, Ni, Mo, etc. | Structural shapes and plates |
| Forged Steels | Uniform grain structure; enhanced strength | High-strength applications |
| Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steels | Heat and rapid cooling; tough and strong | High-strength structural uses |
What are The Different Grades of Structural Steel ?
| Steel Type | Key Features | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| A36 Steel | – Low-carbon & Good weldability – Yield strength: 36,000 PSI |
Construction, bridges |
| A572 Steel | – High-strength low-alloy – Yield strength: 50,000 PSI |
Bridges, offshore platforms |
| A992 Steel | – Higher strength than A36 – Yield strength: 50,000 PSI |
Commercial buildings, bridges |
| A500 Steel | – Yield strength: 46,000 PSI – Tensile strength: 62,000 PSI |
Building frames, columns |
| A514 Steel | – High-strength – Yield strength: 100,000 PSI |
Heavy machinery, mining equipment |
| A516 Steel |
– Yield strength: 38,000 PSI – Tensile strength: 70,000 PSI |
Pressure vessels, boilers |
| A242 Steel | – Low-alloy high-strength – Yield strength: 50,000 PSI |
Outdoor structures, marine applications |
| A588 Steel | – Yield strength: 50,000 PSI – Excellent corrosion resistance |
Bridges, infrastructure |
| A709 Steel | – High-strength low-alloy – Yield strength: 50,000 PSI |
Bridges, buildings |
| A913 Steel | – High-strength low-alloy – Yield strength: 50,000 PSI |
Bridges, buildings |
Structural Steel Standards
ASTM Standards of Structural Steel
- ASTM A36
- ASTM A500
- ASTM A572
- ASTM A588
- ASTM A709
- ASTM A992
- ASTM A285
- ASTM A514
- ASTM A516
European (EN) Standards of Structural Steel
- S235JR – EN 1.0038
- S275J2 – EN 1.0145
- S355JR – EN 1.0045
- S235J2 – EN 1.0117
- S275JR – EN 1.0044
- S355J0 – EN 1.0553
- S420M – EN 1.8827
- S355J2 – EN 1.0577
US Standards of Structural Steel
- A283C
- A570Gr40
- A572Gr50
Different Shapes of Structural cold formed steel
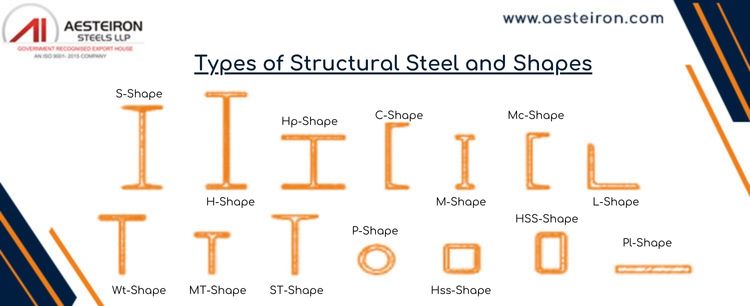
| Shape | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| L-Shape | Corner section; resembles the letter "L" | Construction, industry, mining |
| U-Shape | Two parallel sides; resembles the letter "U" | High durability applications |
| C-Shape | Cross-section resembles the letter "C" | Purlins below roofs |
| Z-Shape | Cross-section resembles the letter "Z" | Purlins, similar uses to C-shape |
| Tubular Hollow Cross-Section | Tubular with hollow cross-section | Multi-axis constructions |
| Flatform | Plates used for attachment | Enhances bearing strength in construction |
| Rectangular Hollow Cross-Section | Rectangular open cross-section | Mechanical and construction industries |
| Square Hollow Cross-Section | Square open cross-section | Columns or pillars |
| Taper-Shaped Beams and Columns | Tapered shape | Industrial prefabricated steel buildings |
S235 Steel Are Designed to Have Good Strength / Weight Ratio
This structural steel grade is known for offering a good strength-to-weight ratio. Its yield strength is 235MPa, which is the maximum load it can bear without permanent damage. This balance between strength and weight makes it ideal for applications where reducing weight is crucial without compromising on durability and strength.
Strength-Weight Ratio of Structural Steel
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Strength divided by density; indicates material efficiency. |
| Purpose | Categorizes materials based on their suitability for specific uses. |
| Example: Concrete | – High compression strength-to-weight ratio. – Less effective in tension strength. – Ideal for compression-focused applications. |
| Usage | Helps determine material suitability for various structural needs. |

Structural Steel vs Stainless Steel
| Aspect | Structural Steel | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Iron + <1.5% carbon | Iron + Chromium, sometimes Nickel, Titanium |
| Common Uses | Beams in high rises, structural applications | Cutlery, medical materials, decorative plates |
| Strength & Hardness | Higher iron content; very hard | Slightly weaker; more malleable at room temperature |
| Ductility | Less ductile compared to stainless steel | Higher ductility due to added nickel |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive due to alloying elements and production |
| Magnetism | Generally magnetic | Typically non-magnetic; some grades may be magnetic |
| Temperature | Higher melting point | Lower melting point, but overlap with structural steel |
Yield Strength of Structural cold formed steel
|
Grade |
Minimum Yield Strength |
|
|---|---|---|
| N/mm2 (MPa) | PSI | |
| S235 | 235 N/mm2 | 33 000 |
| S275 | 275 N/mm2 | 36 000 |
| S355 | 355 N/mm2 | 50 000 |
Tensile Strength of Structural beam
| Grade | Tensile Strength MPa |
|---|---|
| S235 | 360 – 510 MPa |
| S275 | 370 – 530 MPa |
| S355 | 470 – 630 MPa |
Chemical Composition of Structural Steels
| EU Grade | Mn% | C% | Si% | S% | P% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S235 | 1.60 max | 0.22 max | 0.05 max | 0.05 max | 0.05 max |
| S275 | 1.60 max | 0.25 max | 0.05 max | 0.05 max | 0.04 max |
| S355 | 1.60 max | 0.23 max | 0.05 max | 0.05 max | 0.05 max |
Structural Steel Grade E350 Have a Carbon Content Between 0.1 and 0.3%
E250 material Chemical Composition
| Grade | C | S | Mn | P | Si | Carbon Equivalent (CE), Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS 2062 E350 | 0.20 | 0.045 | 1.50 | 0.045 | 0.45 | 0.42 |
S420 Steel Material is Very Durable and is Resistant to Mold, Moisture
This grade of structural steel is known for its durability and resistance to moisture conditions. Due to its chemical composition, it offers excellent protection against environmental factors. This makes it highly suitable for long-term applications in construction where longevity is important.
Advantages and Disadvantages of structural galvanized steel
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Higher strength/weight ratio | Susceptible to corrosion |
| High durability | High fire resistance cost |
| Versatility due to good ductility | High maintenance costs |
| Sustainability | Buckling is an issue |
Benefits of Structural Steel Hollow Sections
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| High Strength-to-Weight Ratio | – Economical due to structural efficiencies. – High radii of gyration enhance compression performance and reduce weight. |
| Aesthetic Appeal | – Favored for architectural use. – Smooth sides, rounded corners, and closed sections are ideal for exposed structures. |
| Less Surface Area for Coatings | – Rectangular and square HSS have ~2/3 the surface area of open sections with similar capacity. – Reduces surface preparation, painting material, labor, and fireproofing. |
| Closed Section | – Effective at resisting torsional loads. – Minimal surfaces collect dust and debris, suitable for clean environments. |
Characteristic of AISI 304 & 316
| Characteristics | 304 stainless steel | 316 stainless steel |
|---|---|---|
| Weldability | High | Good |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent | Even better |
| Magnetic | No | No |
| Hardens during cold forming | Yes | Yes |
| Machinability (annealed) | Fair, but better than 316 | Fair |
| Resists elevated temperatures | High | High |
| Formability | Very good | Good |
| Maximum intermittent service temperature | 1562°F | 1562°F |
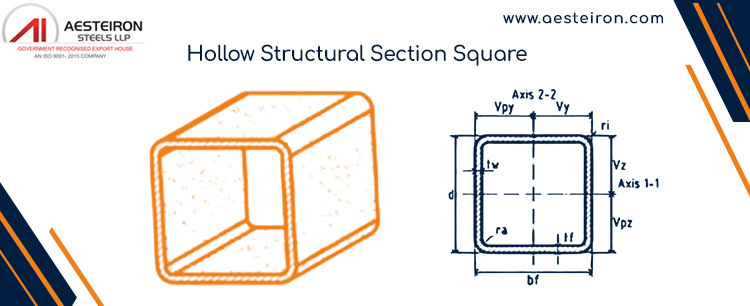
S235 Steel Hollow Section Square Weight Chart
| Section Index | Weight | Area | Sizes | Corner Radius | Axis 1-1 | Axis 2-2 | ||||||||||
| Depth | Width | Thickness | ra | ri | Ix | Sx | rx | ly | Sy | ry | Vpy | Vpz | ||||
| Ax | d | bf | tf | tw | ||||||||||||
| (lb/ft) | (in2) | (in) | (in) | (in) | (in) | (in) | (in) | (in 4) | (in2) | (in) | (in 4) | (in2) | (in) | (in) | (in) | |
| HSSQ22x22x0,875 | 244 7/8 | 67 2/7 | 22 | 22 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 1 5/8 | 4970 | 530 | 8 3/5 | 4970 | 530 | 8 3/5 | 11 | 11 |
| HSSQ20x20x0,75 | 4/7 191 | 52 3/5 | 20 | 20 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 1 2/5 | 3230 | 378 | 7 5/6 | 3230 | 378 | 7 5/6 | 10 | 10 |
| HSSQ22x22x0,75 | 212 | 58 1/5 | 22 | 22 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 1 2/5 | 4350 | 462 | 8 2/3 | 4350 | 462 | 8 2/3 | 11 | 11 |
| HSSQ20x20x0,875 | 221 | 60 4/5 | 20 | 20 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 1 5/8 | 3670 | 433 | 7 7/9 | 3670 | 433 | 7 7/9 | 10 | 10 |
| HSSQ20x20x0,625 | 161 2/5 | 44 2/7 | 20 | 20 | 4/7 | 4/7 | 4/7 | 1 1/6 | 2750 | 320 | 7 7/8 | 2750 | 320 | 7 7/8 | 10 | 10 |
| HSSQ20x20x0,5 | 130 1/2 | 35 4/5 | 20 | 20 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1 | 2260 | 261 | 8 | 2260 | 261 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
S355 Steel Density kg/m3
| Material Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density Ï | ≈ 7850 kg/m3 |
| Unit weight γ | ≈ 78.5 kN/m3 |
| Modulus of elasticity E (Young’s modulus) |
210000 MPa |
| Shear modulus G | G = E / [2 ⋅ (1 + ν) ] ≈ 81000 MPa |
| Poisson’s ratio in elastic range ν | 0.30 |
| Coefficient of linear thermal expansion α | 12 ×10-6 °K-1 |
Mechanical Properties of Steel Grade E350
| Tensile Strength in Mpa | 490 min. |
|---|---|
| Yield Strength in Mpa | 320 min. |
| Hardness in BHN | 170 – 207 |
| Elongation in % | 22 min. |
| Reduction of Area in % | – |
| Impact in Joule | – |
E350 steel Chemical Composition
| Carbon | C % | 0.200 max. |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphorus | P % | 0.045 max. |
| Silicon | Si % | 0.450 max. |
| Manganese | Mn % | 1.550 max. |
| Sulphur | S % | 0.045 max. |
| Iron | Fe % | Balance |
Inspection Checklist of S235 Grade
- Design code
- Purchase order specification
- Steel Structure Manufacture Quality Control Plan
- Steel Structure Inspection and test plan
- Steel Structure Data Sheet
- Steel Structure Approved Drawings
- Steel Structure Strength calculation sheets
- Steel Structure Material Test Reports
- Certificate No.
- Heat or cast No.
- Chemical composition.
- Mechanical properties.
- Heat treated condition.
- NDE applied and results.
- Welders properly qualified
- Test coupons compiled where necessary
- Dimensional check on pre-drilled parts
- Correct fastening being used
- Protection of protruding parts
- Shipping and other marks
Structural Steel and Reinforcement Steel Difference

| Aspect | Structural Steel | Reinforced Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Forming the frames of buildings and structures | Reinforcing concrete and masonry structures |
| Materials | Various types of steel, including carbon-manganese, high-strength low-alloy | Hot rolled deformed bars, mild steel plain bars, cold worked steel reinforcements |
| Forms | Beams, braces, plates, columns in various shapes (S, L, H, C, I, HSS, T, Pipe) | Steel bars (rebar) in various forms and treatments (hot rolled, cold worked, etc.) |
| Shapes | Defined by cross-sectional shapes such as S, L, H, C, I, HSS, T, Pipe | Typically round or square bars, not defined by cross-sectional shapes |
| Key Characteristics | High strength, flexibility | Provides tensile strength to complement concrete’s compressive strength |
| Typical Applications | Used in constructing beams, columns, bridges | Used within concrete to handle tensile stresses, e.g., in slabs, beams |
| Strength Focus | Focuses on overall structural strength and load-bearing capacity | Focuses on tensile strength and reinforcing concrete’s performance |
| Compatibility | Can be used alone or with concrete and Company Profile
We are the largest exporter of used construction machinery in Shandong Province, China, with many years of industry experience. Our warehouses are located in Shanghai and Heilongjiang Province, specializing in the export and domestic markets of used machinery for over 20 years. Main Business Our main business includes: used excavators, used wheel loaders, used graders, used bulldozers, used road rollers, used forklifts, used backhoe loaders, used tippers, used concrete pumps, used cranes, used buses, and more. You have found a high-quality supplier of used machinery. We are a top-tier supplier in the industry, with over 50 branches across China. Our Advantages We offer the lowest prices and the best quality in the market, with products covering almost all brands and specifications, including SANY, Liugong, XCMG, SDLG, Caterpillar, Komatsu, Volvo, Hitachi, Doosan, Hyundai, Mitsubishi, Sunward, Kubota, and more. Whatever type of machinery you need, we can meet your requirements without hesitation. Markets and Clients Our main markets include Central Asia, the CIS, Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. The machinery we sell has received unanimous praise from our customers. With over 20 years of loyal customers, we appreciate your trust and support! used machinery for sale,small excavator for sale,used excavators for sale near me,used excavators for sale by owner,used mini excavator Shandong Vio Machinery co.,ltd. , https://www.shantui-xcmgparts.com |
