Quick Connect Fittings: Enhancing Efficiency in Hydraulic Systems
In the fast-paced world of hydraulic systems, efficiency and reliability are crucial. Among the many components that contribute to this, quick connect hydraulic fittings have become a game-changer. These fittings are designed to allow fast and secure connections in hydraulic lines, making system maintenance easier and operations more efficient. Let’s take a closer look at how these fittings work and why they’re essential for modern hydraulic applications.
The Simple Mechanics Explained
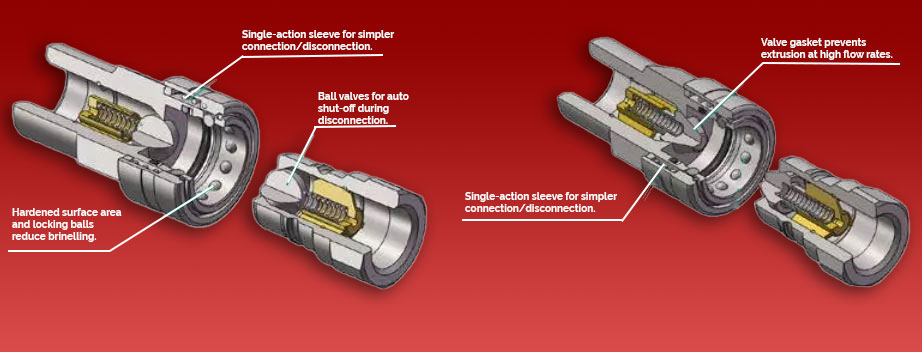
The operation of quick connect fittings is both simple and effective. They typically consist of two parts: a male plug and a female coupler. When the male plug is pushed into the female coupler, it locks automatically, creating a secure connection. Inside the coupler, there are usually ball bearings or similar mechanisms that grip the male end, ensuring a tight seal and preventing leaks. This locking mechanism also helps maintain pressure within the system. To disconnect, you simply press or pull a release button or sleeve on the coupler, which disengages the locking mechanism and allows the male plug to be removed easily. This feature makes assembly and disassembly quick and tool-free, reducing downtime during maintenance or system changes.
Materials Matter: Choosing the Right Quick Connect Fittings for Your Hydraulic System
When it comes to quick connect fittings, the materials used play a key role in their performance and longevity. Common options include brass, which offers good corrosion resistance and is suitable for general use; plastic, which is lightweight and cost-effective but better suited for less demanding environments; and stainless steel, known for its strength, durability, and excellent resistance to corrosion. Stainless steel fittings are especially popular in harsh conditions where exposure to extreme temperatures or corrosive fluids is common. They can withstand high pressures and resist wear over time, making them ideal for critical hydraulic applications. Additionally, these fittings come in various designs, such as straight connectors, elbows, and tees, to suit different installation needs and space constraints.
Conclusion
Quick connect fittings are an essential part of modern hydraulic systems due to their versatility, ease of use, and ability to reduce downtime. Their design allows for fast, tool-free connections and disconnections, which is especially valuable in industrial settings where efficiency is key. By enabling quick maintenance and reconfiguration, these fittings help improve productivity and system reliability. Whether you're working with heavy machinery or complex fluid power systems, incorporating quick connect fittings can significantly enhance performance and safety. Overall, they represent a smart and practical solution for anyone looking to optimize their hydraulic setup.

Frequently Asked Questions:
How do hydraulic quick couplers work?
Answer: Hydraulic quick couplers are designed for fast and secure connections in hydraulic systems. They consist of two parts: a male plug and a female coupler, each equipped with a closed valve. When the male plug is inserted into the female coupler, the valves open automatically, allowing fluid to flow. A locking mechanism inside the coupler secures the connection, while seals ensure a leak-proof joint. To disconnect, a release mechanism on the coupler is activated, which retracts the locking device and closes both valves, stopping the flow of fluid. These couplers are perfect for applications that require frequent, tool-free connections and disconnections, offering efficiency and reliability without compromising safety.
How to disconnect quick connect fittings?
Answer: Disconnecting quick connect fittings is a straightforward process, but it should always be done safely. First, locate the release mechanism on the female coupler, which could be a button, ring, or sleeve. Make sure the hydraulic system is fully depressurized before attempting to disconnect, as doing so under pressure can be dangerous and may damage the fitting. Once the system is safe, engage the release mechanism by pushing or pulling it, depending on the design. While holding the release in place, gently pull the male plug out of the coupler. After disconnecting, inspect both ends of the fitting for any signs of wear or damage. If needed, replace the parts to ensure a secure and leak-free connection next time. Always follow the manufacturer's guidelines, as different models may have specific instructions.
Basic use: About 50% of the tungsten ore mined in the world is used for the smelting of high-quality steel, about 35% is used for the production of hard steel, about 10% is used for making tungsten wire, and about 5% is used for other purposes. Tungsten can be used to manufacture firearms, rocket propeller nozzles, armor-piercing bullets, metal-cutting blades, drills, superhard dies, wire drawing dies, etc. Tungsten is widely used in mining, metallurgy, machinery, construction, transportation, electronics, chemical industry, Light industry, textile, military industry, aerospace, science and technology, various industrial fields.
Tungsten is widely used in modern technology in pure metal state and alloy system state. The most important alloy system state is alloy steel, tungsten carbide-based cemented carbide, wear-resistant alloy and strong heat alloy. Tungsten is mainly used in the following industrial fields:
Steel industry: Tungsten is mostly used in the production of special steel. The widely used high speed steel contains 9%-24% tungsten, 3.8%-4.6% chromium, 1%-5% vanadium, 4%-7% cobalt, 0.7%-1.5% carbon. The characteristic of high-speed steel is that it can be automatically quenched at a high tempering temperature (700-800℃) in the air, so it maintains high hardness and wear resistance until 600-650℃. Tungsten steel in alloy tool steel contains 0.8%-1.2% tungsten; chromium-tungsten silicon steel contains 2%-2.7% tungsten; chromium-tungsten steel contains 2%-9% tungsten; chromium-tungsten-manganese steel contains 0.5%- 1.6% tungsten. Tungsten-containing steel is used to manufacture various tools: such as drills, milling cutters, wire drawing dies, female and male dies, air tools and other parts. Tungsten magnet steel is a permanent magnet steel containing 5.2%-6.2% tungsten, 0.68%-0.78% carbon, and 0.3%-0.5% chromium. Tungsten-cobalt magnets contain 11.5%-14.5% tungsten, 5.5%-6.5% molybdenum, and 11.5%-12.5% cobalt hard magnetic materials. They have high magnetization and coercivity.
Tungsten Particle,Low Carbon Tungsten Particles,Iron Alloy Tungsten Particles,High-Purity Tungsten Particles
Jiangsu Lucky Metal Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.luckymetalmoly.com
