Ever thought about how certain car parts are so vital that your vehicle simply won’t function without them? The alternator falls squarely into that category. This small yet essential component plays a dual role: it powers your entire car while it’s running, and simultaneously charges the battery. Without it, you’d be stuck—literally.
If you’re curious about alternators and want to learn more, you’ve come to the right place. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about these critical parts.
What Exactly Is an Alternator?
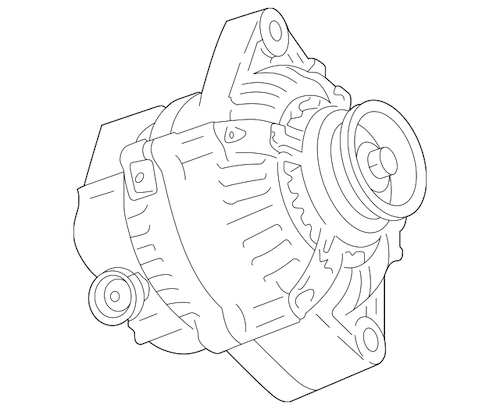
Toyota alternator #27060-74750-84: for 1998-2000 RAV4s
Mounted on the engine with a pulley, the alternator acts as a compact generator. Its primary job is to supply electricity to all the car’s electrical systems, including the dome lights, dashboard instruments, air conditioning fans, radio, power windows and seats, brake lights, headlights, and turn signals. While the battery initially powers these systems, the alternator ensures they stay charged during operation.
What Does an Alternator Look Like?

A typical Toyota alternator is roughly the size of a grapefruit and weighs around six pounds. Despite its small size, it packs quite a punch. Although designs vary slightly depending on the Toyota model, all alternators share two key features: numerous ventilation holes to keep the unit cool, and a central rotor that spins to generate electricity.
Inside every alternator, there are four main components:
- Stator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Rotor: The spinning part that generates electromagnetic fields.
- Diode: Converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
- Voltage Regulator: Ensures the output voltage remains consistent.
How Does an Alternator Function?
As soon as you start the engine, the alternator kicks into gear. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- The ignition switch turns on.
- The engine starts running, and the drive belt spins the alternator pulley.
- The rotor, connected to the pulley, begins rotating, creating electricity through electromagnetic induction.
- This electricity moves through the stator to the diode, where it’s converted from AC to DC.
- The regulated DC current travels to the car battery via the voltage regulator.
- Finally, the battery supplies power to the vehicle’s electrical systems.
Do Alternators Ever Fail?
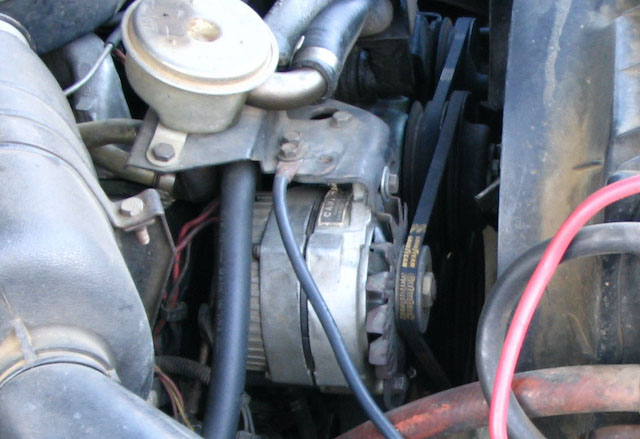

An alternator in action. Source: Phasmatisnox via Creative CommonsÂ
Alternators usually last between 100,000 and 150,000 miles, but they’re not immune to wear and tear. Over time, various internal components can degrade, leading to failure. Some common culprits include:
- Worn-out alternator pulleys
- Faulty diodes
- Malfunctioning voltage regulators
- Damaged stators
- Loose or worn bushings
- Defective coils
- Loosened or damaged bearings
In rare cases, an alternator might fail prematurely due to mishandling during installation. For instance, if the pulley is tightened too much, it could snap. Similarly, a dropped alternator might suffer internal damage like broken connections or loose bearings.
How Much Does a New Alternator Cost?
A brand-new OEM alternator for a Toyota can range anywhere from $150 to $900, depending on the specific model. If you’re looking to save money, consider purchasing a remanufactured option instead. These units are often just as reliable but significantly cheaper.
For the best deals, shop online rather than visiting a dealership. Dealerships tend to mark up their parts, whereas authorized sellers like us operate with lower overhead costs. As a result, we’re able to offer competitive prices—and sometimes even wholesale pricing. Plus, we stock refurbished alternators alongside new ones. Check out our catalog today to find the perfect fit for your Toyota!
Written by Jason Lancaster
Laser Welding Machine,Aluminum Laser Welder Machine,Fiber Welding Machine,High Power Laser Welding Machine
Herolaser , https://www.herolasermachine.com
