Inspection Tools: A Guide to the Tools Inspectors Use in Their Daily Work
Inspection tools help inspectors collect the data they need to ensure the proper maintenance of the assets they're inspecting—Read this guide for an overview of the different types of inspection tools they use.
Inspection tools play a crucial role in gathering essential data that helps maintain the integrity and safety of various assets. Whether it's visual, thermal, or thickness measurements, these tools are designed to meet specific inspection needs.
The type of data required will determine the tools used. For instance, if the goal is to detect corrosion, thermal imaging or ultrasonic sensors might be necessary. Once the data is collected, inspectors analyze it to assess the condition of the asset and decide on the appropriate maintenance actions.
After collecting data, inspectors examine it to understand the condition and maintenance status of the thing they are inspecting. This process ensures that any potential issues are identified and addressed before they become critical.
Inspection Tools vs. Inspection Equipment
For the purposes of this article, inspection tools refer to the actual instruments used by inspectors to collect data. These can range from simple measuring devices to advanced drones equipped with cameras and sensors.
On the other hand, inspection equipment includes anything that supports the inspector’s work, such as tool belts, scaffolding, or ropes used for access. While tools are directly involved in data collection, equipment provides the necessary support to perform inspections safely and effectively.
[Related read: Confined Space Equipment: A Guide]
Whether it's a large industrial boiler or a residential HVAC unit, the process remains similar: collect data, analyze it, and make informed maintenance decisions.
Although the core idea is straightforward, the variety of tools used can be vast, depending on the type of data needed. Some tools are organized by the data they collect, while others are categorized by their method of operation, like aerial or ground-based robotics.
Now let's take a closer look at the most commonly used inspection tools across industries.
Â
Cameras and Other Visual Data Collection Tools
Visual data is one of the most frequently collected types during inspections. Cameras are the primary tool for this purpose, but not all cameras are suitable for every task.
The choice of camera depends on the specific requirements of the inspection. Factors like image quality, low-light performance, and color accuracy can influence the selection.
Here are some common visual data collection tools:
-
Digital cameras. High-quality digital cameras are essential for capturing clear images. They come in various forms, from basic models to high-end professional ones.
-
Borescopes. These flexible tubes allow inspectors to see into hard-to-reach areas, making them invaluable for internal inspections.
-
Video and digital microscopes. These tools provide magnified views, allowing detailed examination of small components.
-
Videoscopes. Similar to borescopes, videoscopes offer remote viewing capabilities, ideal for inspecting confined spaces.
-
CCTV. Closed-circuit television systems are widely used in sewer and pipe inspections, enabling remote viewing of underground infrastructure.
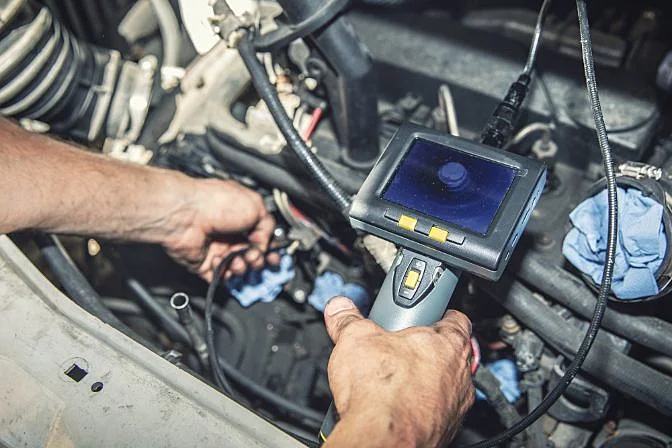 A borescope being used to inspect a car engine
A borescope being used to inspect a car engine
Other NDT Sensors and Testing Methods
While visual data is common, other types of data may be necessary for comprehensive inspections. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods and specialized sensors are often used to gather this information.
Ropes and Drones Case Study
A recent inspection by Premium Inspection & Testing showcased the effectiveness of combining drones and rope access. The team used a drone to collect initial visual data inside a coke drum, followed by manual inspections using ropes to gather more detailed information.
This approach not only saved time but also reduced costs significantly, highlighting the value of integrating multiple tools into a single inspection strategy.
Here are some examples of NDT methods and sensors used in inspections:
-
Thermal data. Thermal sensors detect heat patterns, useful for identifying leaks or overheating areas.
-
Ultrasonic data. Ultrasonic testing uses sound waves to detect internal flaws or measure material thickness.
-
Radiography data. X-ray or gamma-ray imaging helps identify internal defects in materials.
-
Eddy current data. Eddy current testing detects surface and near-surface flaws using electromagnetic induction.
These tools are essential for ensuring the structural integrity of assets across various industries.
Robots
Robotic solutions have revolutionized the inspection industry, offering safer and more efficient ways to collect data. There are three main categories of robotic tools used by inspectors:
-
Drones / Aerial Robotic Solutions
-
Ground-Based Robotic Solutions
-
Submersible / Underwater Robotic Solutions
Drones / Aerial Solutions
Drones have become a staple in industrial inspections due to their ability to reach difficult-to-access areas. They are particularly useful for visual inspections, though some models can also capture thermal or other sensor data.
Why use RVI tools?
There are several advantages to using drones for inspections:
-
Safety. Drones reduce the need for human exposure to hazardous environments.
-
Savings. Using drones can cut inspection costs significantly.
-
Reduced downtimes. Drones speed up the inspection process, minimizing operational downtime.
Indoor vs. outdoor drones
Indoor drones are designed for confined spaces and feature collision-resistant designs. Outdoor drones, on the other hand, are built for open environments and lack the same level of protection.
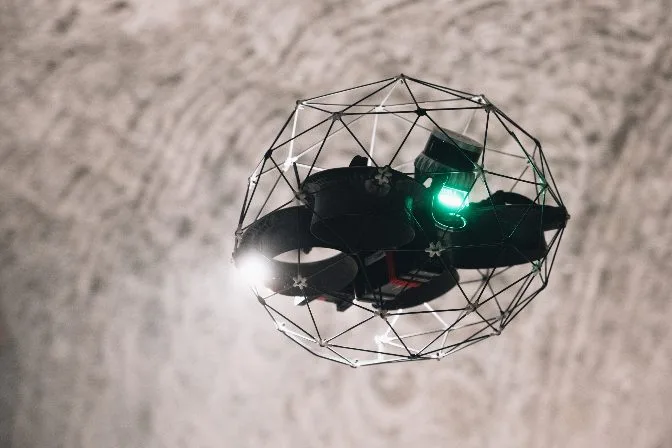

Outdoor drones, such as the DJI Matrice 300, are popular for large-scale inspections.
 DJI's Matrice 300, an outdoor drone commonly used in inspections
DJI's Matrice 300, an outdoor drone commonly used in inspections
Ground-based Robotic Solutions
Ground-based robots offer similar benefits to drones, improving both safety and efficiency during inspections.
Some examples include the Inuktun MaggHD, Deep Trekker DT320, and Inuktun Versatrax 150, each designed for specific inspection tasks.
Robots—Submersible Solutions
Submersible robots are increasingly used in underwater inspections, providing safe and effective alternatives to diving operations.
Examples include the MASKI+ and the Intero Tank Explorer, which are used in challenging environments like hydro dams and petrochemical tanks.
Recent Advances in Robotics
Advancements in robotics continue to expand the possibilities for remote inspections. New tools are being developed to handle even the most hazardous or inaccessible locations.
Some robots can now not only detect issues but also perform minor repairs, such as clearing debris or applying UV-cured patches.
Measuring Devices
Measuring devices are essential for collecting precise dimensional data. These tools range from simple hand-held calipers to sophisticated digital gauges.
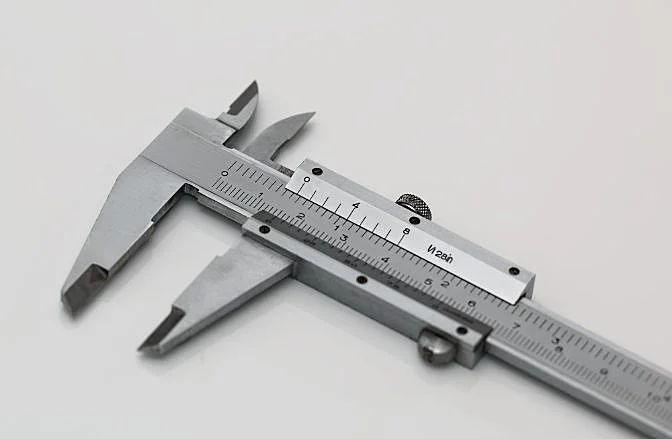
Common measuring devices include engineering squares, protractors, levels, calipers, gages, and micrometers. Each serves a unique purpose in ensuring accurate measurements.
Inspection Software
As the volume of inspection data grows, software has become an essential part of the process. Modern tools streamline data collection, analysis, and management, making inspections faster and more efficient.
Improved Data Collection Software
Software like Flyability Inspector 3.0 integrates 3D modeling to visualize assets and identify defects quickly. These tools enhance the inspection experience by providing real-time insights.
Data Management Tools
Advanced software solutions use AI and machine learning to process large datasets efficiently. This enables faster decision-making and improves overall inspection outcomes.
With continuous innovation, inspection software is playing a key role in enhancing safety, reducing costs, and improving the quality of inspections across industries.
Full Electric Stackers(Walkie Type)
Full electric stackers, also known as walkie stackers, are powered material handling equipment used for lifting and transporting pallets and loads within a warehouse or industrial setting. Unlike traditional forklifts, full electric stackers do not require a dedicated operator seat and are operated by a pedestrian walking alongside or behind the equipment.
These stackers are powered by electric motors and are equipped with a battery that provides the necessary power to lift and move loads. They are designed to be compact and maneuverable, making them ideal for use in narrow aisles and tight spaces.
Full electric stackers typically have a lifting capacity ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 pounds, although some models can handle heavier loads. They are equipped with forks or platforms that can be raised and lowered to lift and stack pallets or other loads. Some models also feature adjustable forks or platforms to accommodate different load sizes.
These stackers are designed with safety features such as brakes, emergency stop buttons, and load backrests to prevent accidents and ensure the safe handling of loads. They also often come with features like adjustable steering handles, easy-to-use controls, and ergonomic designs to enhance operator comfort and efficiency.
Full electric stackers offer several advantages over other types of material handling equipment. They are quieter and produce zero emissions, making them suitable for indoor use and environmentally friendly. They also require less maintenance compared to internal combustion-powered equipment, reducing downtime and operating costs.
Overall, full electric stackers are versatile and efficient tools for lifting and moving loads in warehouses, distribution centers, and other industrial settings. They provide a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for material handling needs.
Walkie Stacker,Electric Stacker,Full Electric Stacker,Electric Walkie Stacker
Jiangsu Lundi Forklift Co.,Ltd. , https://www.lundilift.com
