Updated 30-09-2022
Electric mobility is no longer a distant dream. Today, electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly becoming the standard choice for drivers around the world. With the global EV fleet expected to exceed 20 million this year, it's clear that the shift to electric is accelerating.
Switching from gas stations to charging your EV can feel quite different and even a bit overwhelming at first. To help you understand better, we’ve compiled the seven most common questions about electric car charging:
- How does electric charging work?
- What powers electric car charging stations?
- How long does it take to charge an EV battery?
- What does it cost to charge an electric car?
- How often do you need to charge an electric car?
- Where can I charge my electric car?
- How much maintenance do EV chargers require?
1. How does electric car charging work?
Charging an electric vehicle is a straightforward process, but it varies depending on the type of charger. Most EVs come with a cable and plug that match your car and country’s standards. You can usually plug it into a regular home outlet and charge directly from your household electricity.
How do EV charging stations work?
Charging at public stations or at home involves a few steps. First, you identify yourself using an app, RFID card, or contactless payment. Then, connect the cable to both the station and your car. Once connected, the charging begins, and you’ll see confirmation on your car’s display and the station’s lights. After charging, you can end the session via the app or the station itself.
A new technology called Plug & Charge (ISO 15118) is changing the game by allowing automatic recognition and connection between your car and the charger, making the process faster and more seamless.

How do you pay for electric car charging?
At home, your EV charging will add to your electricity bill. For public stations, you might pay via app, card, or through a subscription. Some places even offer monthly billing based on usage.
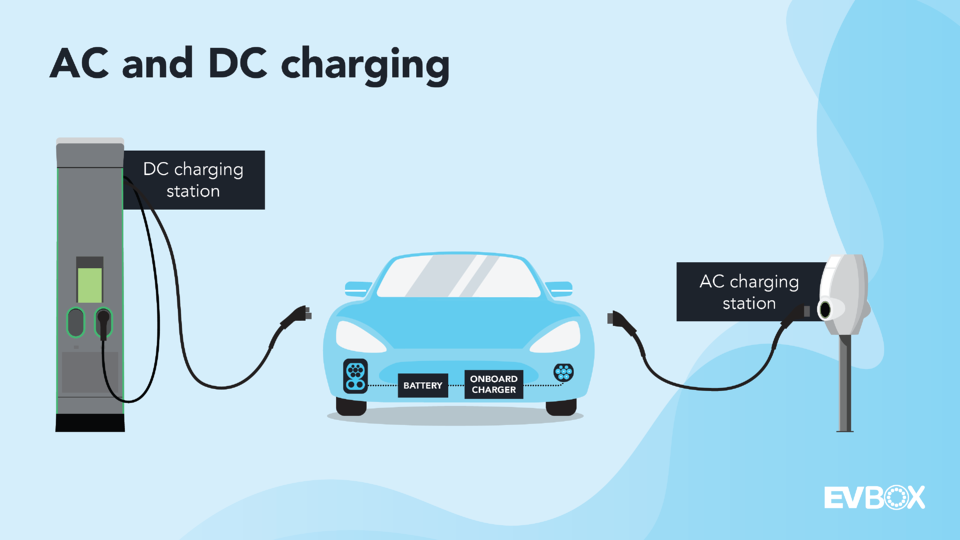
2. What powers electric car charging stations?
EV chargers operate on either AC or DC power. The main difference lies in how the power is converted before reaching your car’s battery. AC chargers convert power inside the vehicle, while DC chargers do it at the station, enabling faster charging.
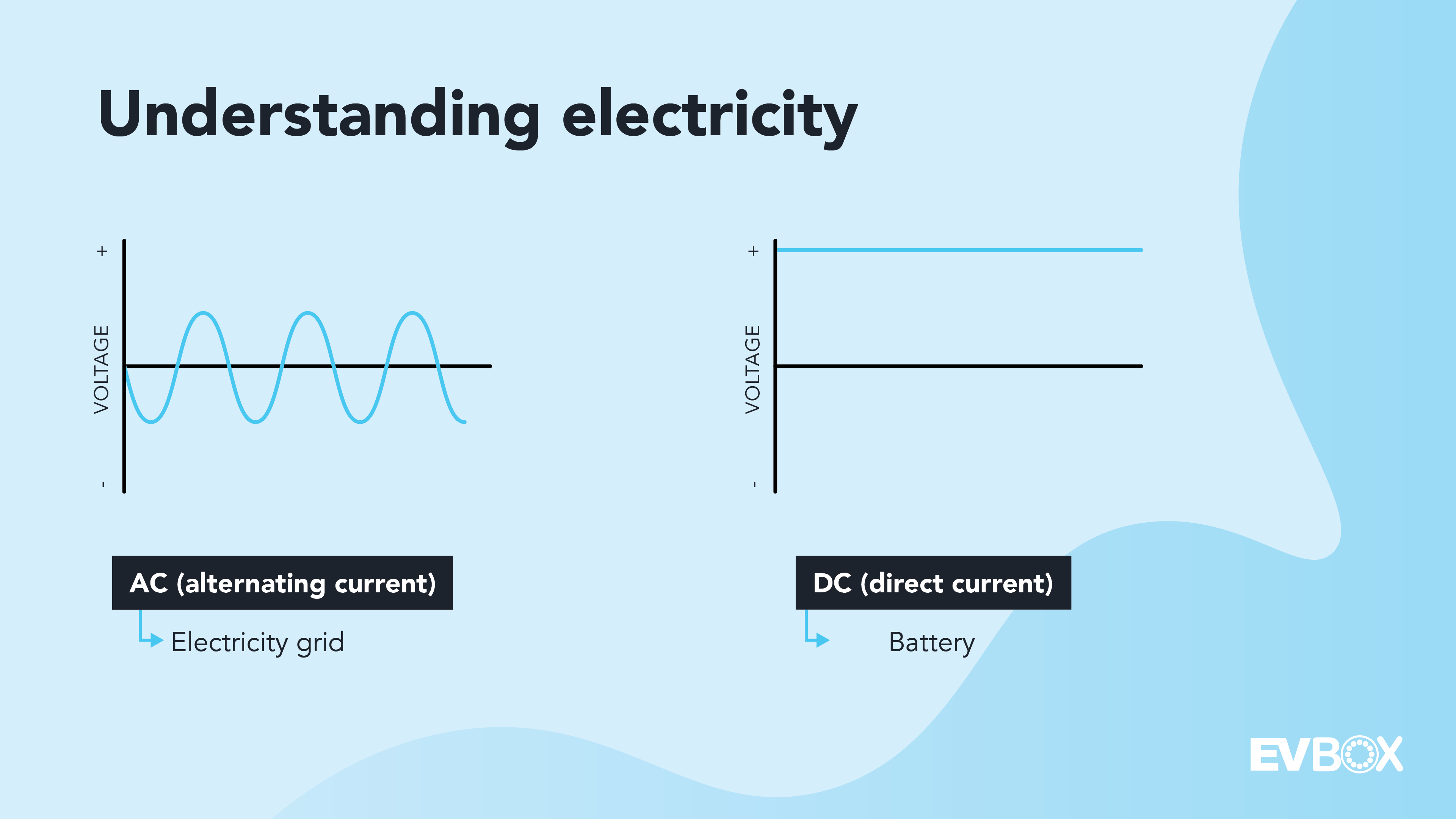
AC vs DC electricity
All EV batteries store DC power, so the grid’s AC must be converted. This conversion happens differently depending on the charger type. AC chargers are slower because they rely on the car’s onboard converter, while DC chargers handle the conversion externally, delivering much higher speeds.
For example, a Tesla Model S with a 100 kWh battery would take about 7 hours with a 22 kW Level 2 charger, but only 30 minutes with a 350 kW DC fast charger.
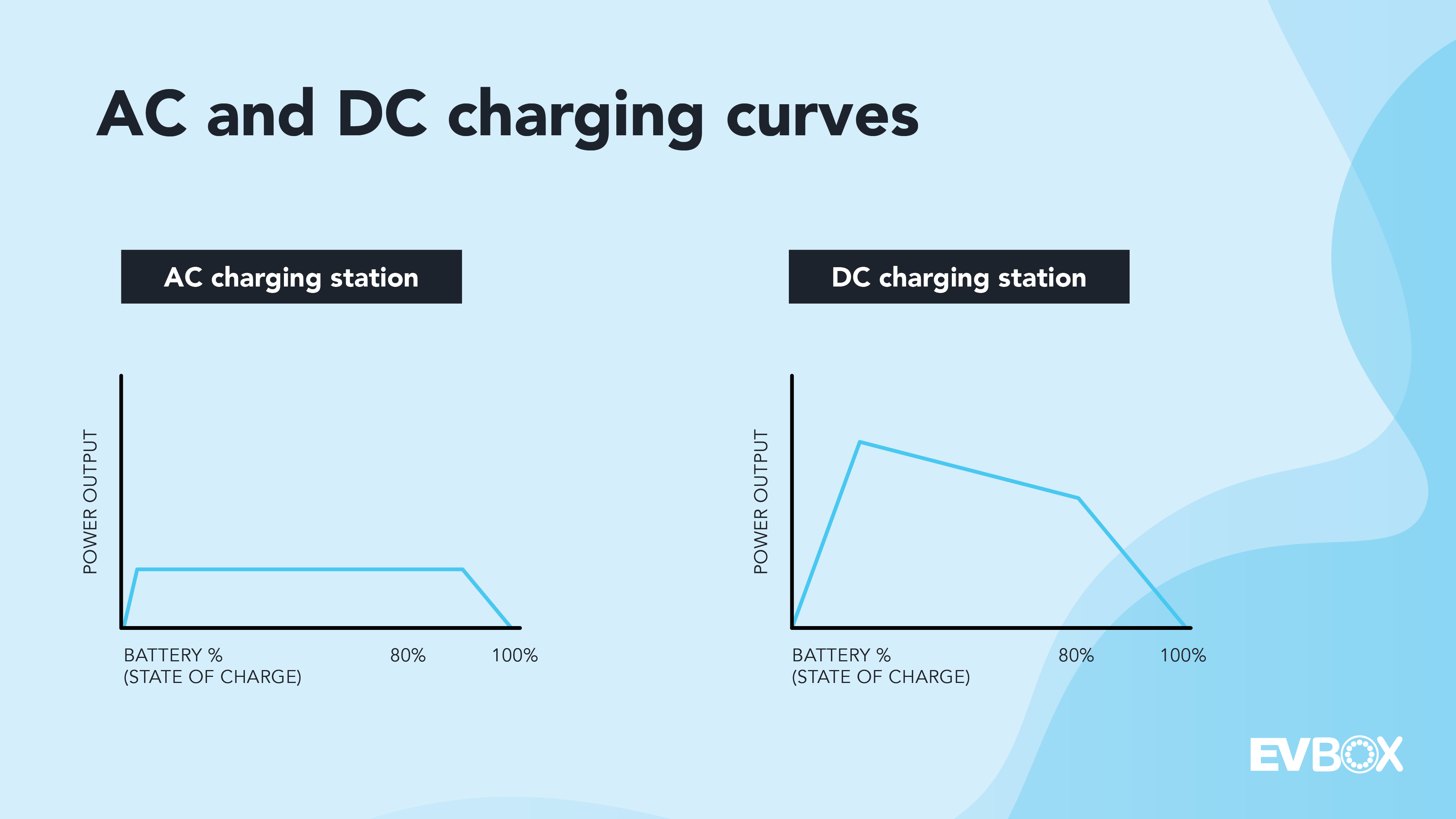
3. How long does it take to charge a car battery?
Charging time depends on several factors, including battery size, state of charge, and the charger’s power. Larger batteries take longer, and charging slows down as the battery nears full capacity.
For instance, charging from 20% to 70% may take just a few minutes, but going from 70% to 100% could take significantly longer. Also, not all EVs can accept the same charging speed—some can take up to 350 kW, while others are limited to lower rates.
EV charger types
There are three main types of chargers:
- Level 1: Slowest, uses a regular wall socket, adds about 6–8 km per hour.
- Level 2: Faster, needs professional installation, adds 40–120 km per hour.
- Level 3: Fastest, uses DC power, can charge up to 80% in under an hour.
Weather also affects charging speed, especially extreme temperatures. Batteries perform best around 21°C, and outside this range, they use energy to regulate their temperature, which can slow down the process.
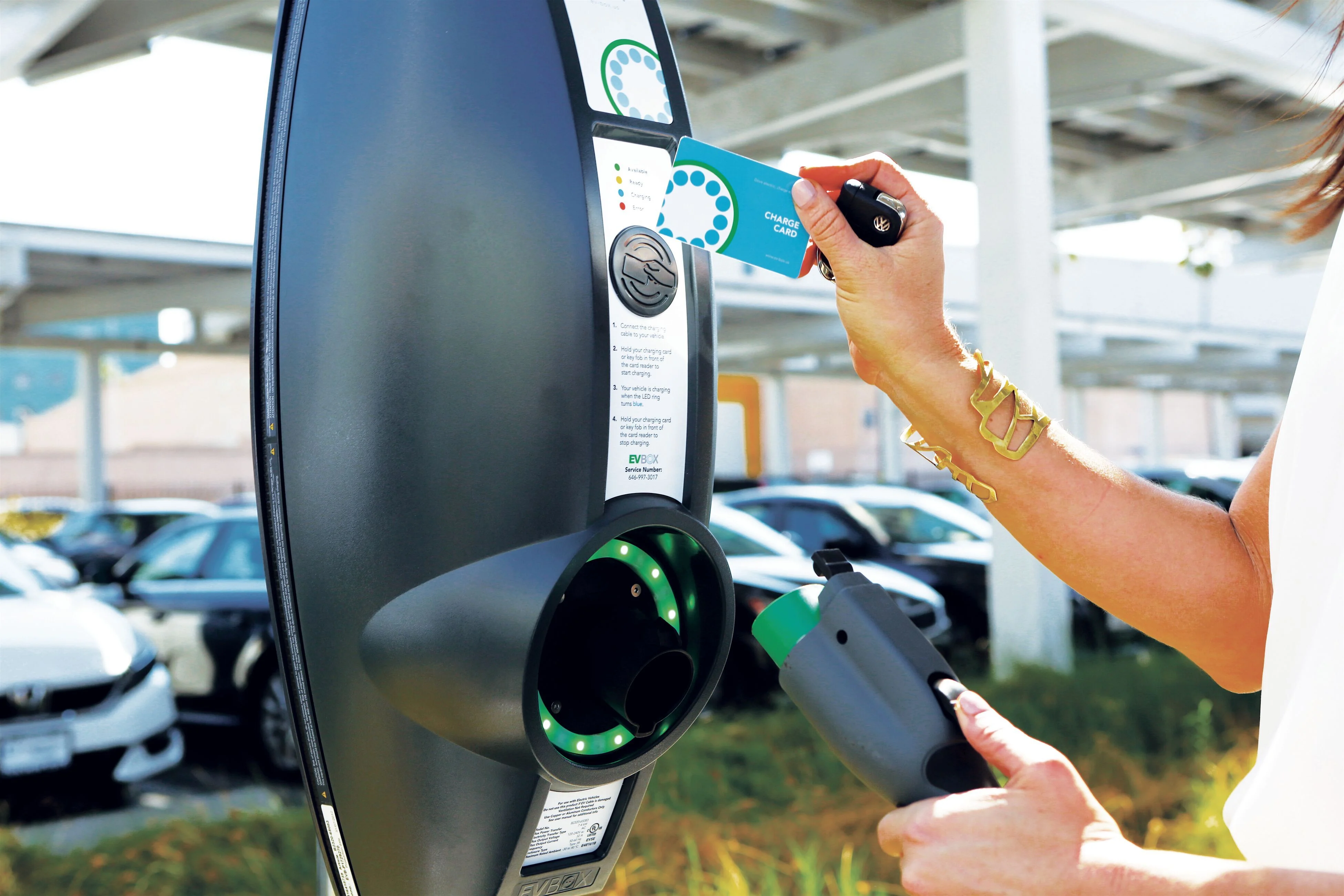
4. What does it cost to charge an electric car?
Costs vary depending on location, utility provider, and charger type. On average, a full charge can cost around €30 or $30, though home charging is typically cheaper. In the EU, the average price is around 40 cents per kWh, while in the US, it’s about 17 cents.

Cost to charge an electric car
A 50 kWh battery like the Tesla Model 3 would cost about €20 or $8.5 to fully charge at home. Public and fast chargers tend to be pricier, with a full charge costing around €30 or $30. However, overall, EV charging is still much cheaper than fueling a gasoline car.
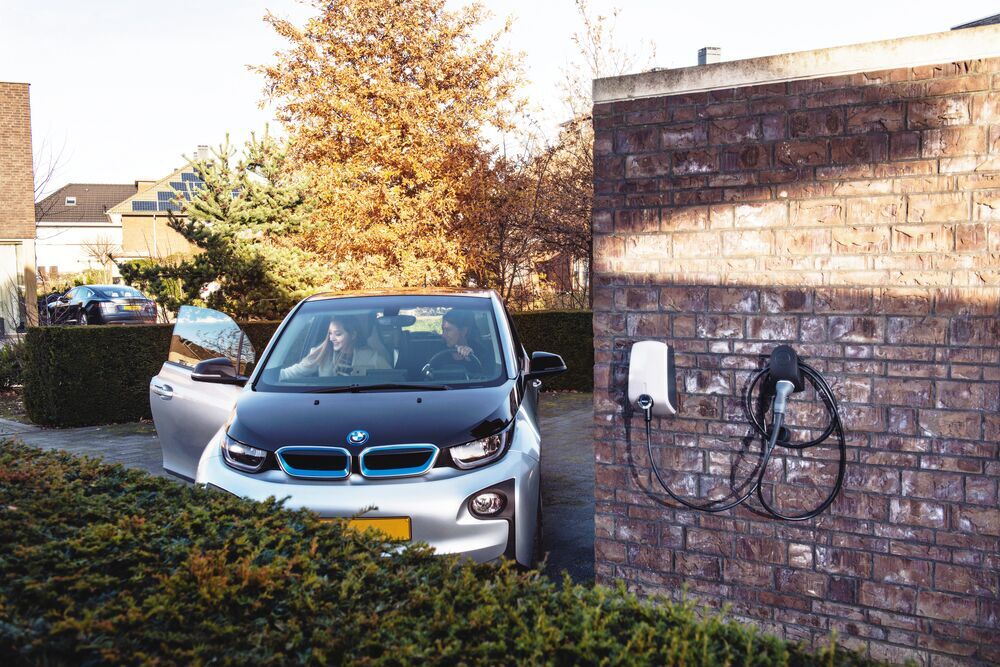
5. How often do you have to charge an electric car?
It depends on your driving habits and the car’s range. The average EV range is around 331 km, and many daily trips are well within that range. If you drive short distances, you may only need to charge once a week. However, if you drive more or have a smaller battery, you may need to charge more frequently.

6. Where can I charge my electric car?
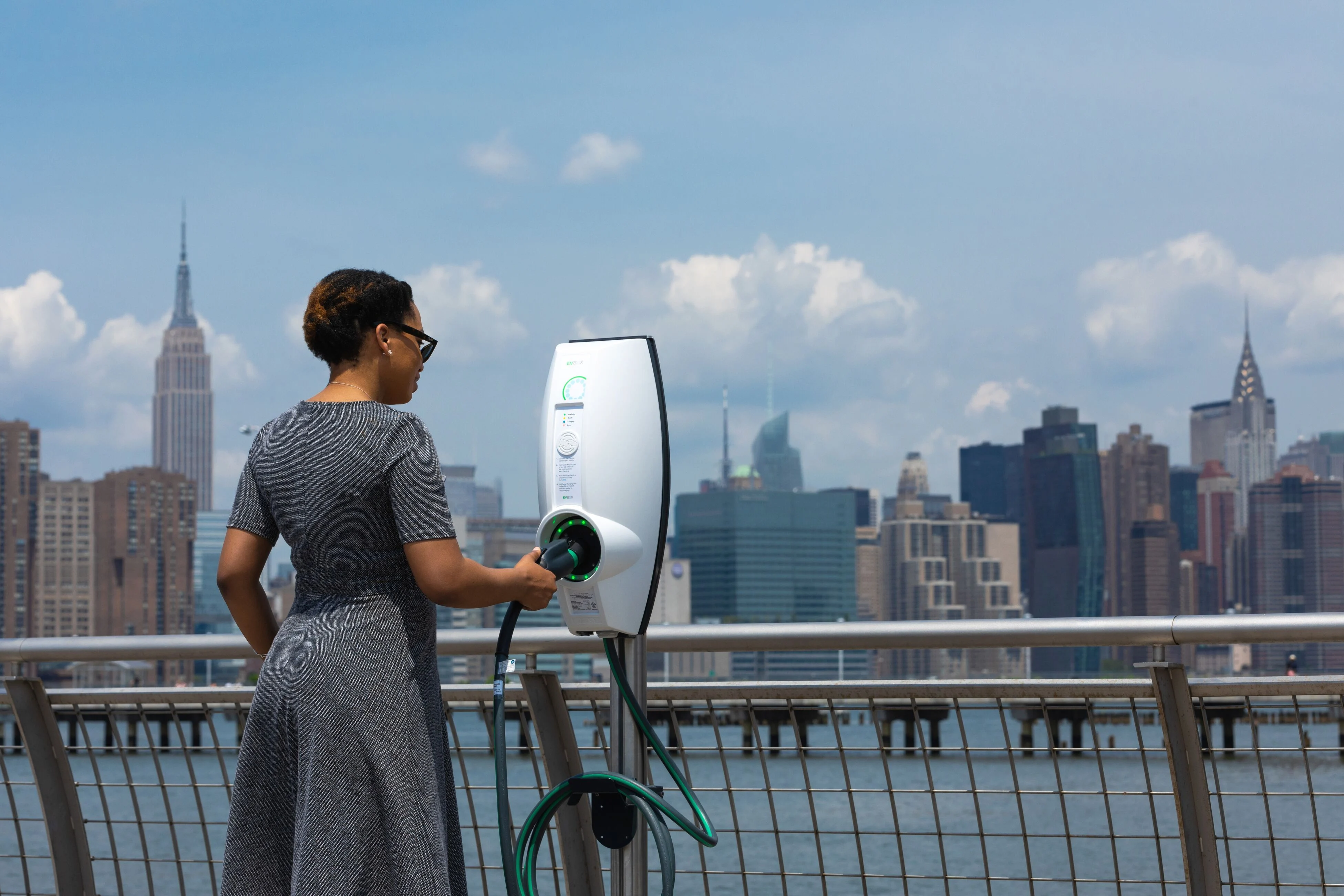
With electricity available almost everywhere, there are countless options for charging. According to our Mobility Monitor report, 64% of EV owners charge at home, 34% at work, and 31% at public locations like shopping centers and gas stations.

7. How much maintenance does an EV charger need?
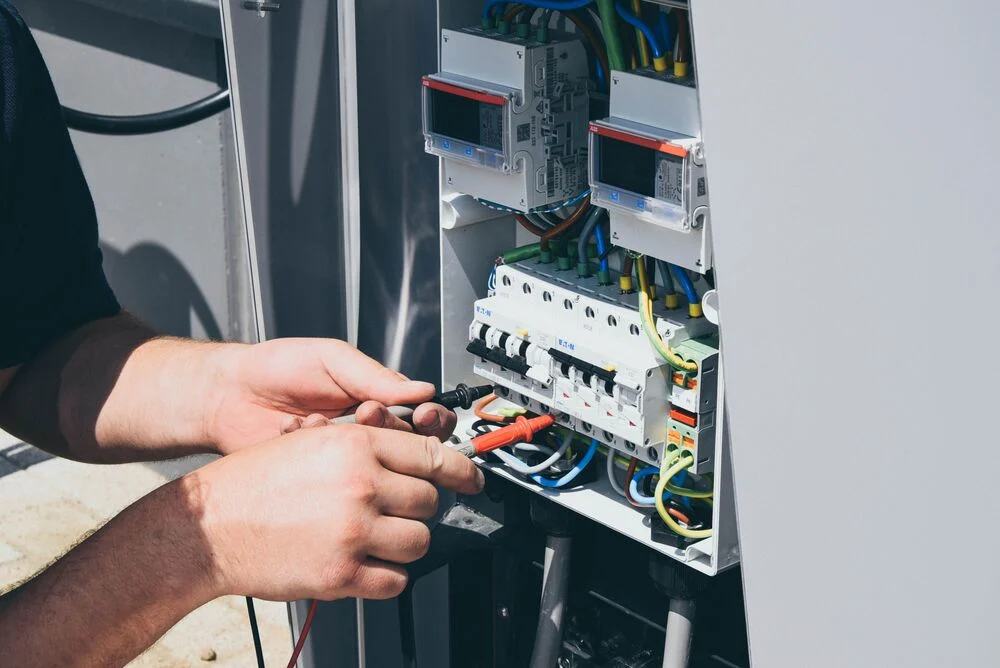
Most EV chargers require very little maintenance. Home Level 1 and 2 chargers should be checked occasionally for damage, but they’re built to last years. Public chargers need more regular checks, especially for cables, software, and user interfaces.
Many manufacturers offer service plans and remote diagnostics to keep things running smoothly. Overall, maintaining an EV charger is simple and rarely an issue.

Switching to electric mobility brings changes, but it also offers flexibility and convenience. Charging an EV is different from refueling a gas car, but it can easily fit into your lifestyle. These are the top 7 questions about EV charging. If you have more, check out our complete guide for more details.







